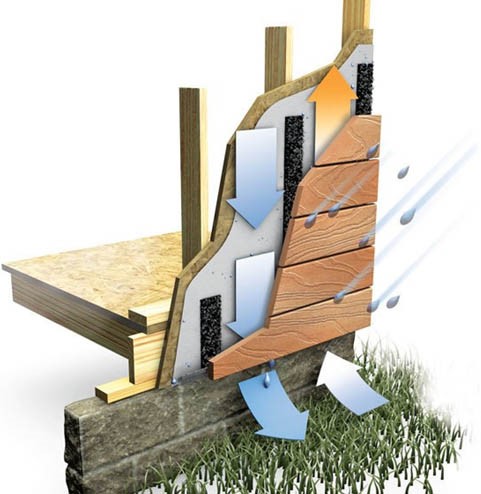
A rain-screen system is a building technique to manage moisture in exterior wall assemblies. It is a secondary weather-resistant barrier installed behind the exterior cladding of a building, allowing for air to circulate between the cladding and the structural wall. This creates a drainage gap that helps prevent moisture from penetrating the wall assembly while allowing any moisture that does penetrate to dry out quickly. Rains-screen systems are commonly used in British Columbia due to the country’s cold and wet climate, which makes managing moisture in building envelopes particularly important for preventing damage and increasing energy efficiency.
The main parts of a rain-screen system include:
- Cladding: The outermost layer of the building envelope that protects the building from the elements.
- Air gap: A gap between the cladding and the rest of the building envelope that allows for ventilation and drainage of any moisture that may seep into the system. This gap is mainly created by Pressure-treated wood strips, Metal Z-girts, Special clips or unique drainage mats usually used for Cedar shingles or vertically installed wood.
- Exterior insulation: Materials installed on the exterior of a building. It is a method of increasing the insulation capabilities of the building that can provide several benefits, including improved energy efficiency, reduced energy consumption, increased comfort, and better moisture management.
- Weather resistive barrier: A layer that is placed behind the cladding to prevent moisture from penetrating the building envelope.
